100 % producers 10% primary consumers 1% secondary consumers.
producers ----> Primary consumers -------> secondary consumers. (all has to follow the process of respiration)
All organisms die and breaks down by micro - organism
Energy is lost by respiration
Total Pageviews
Wednesday, May 18, 2011
4.6 Energy and substances in food chains
Bush grass been eaten by impala which is the producer and primary consumer.
cheetah is the secondary consumer
lion is the tertiary
Converts light energy to chemical energy.
Chemical energy takes the form of organic molecules including carbohydrates, proteins and lipids.
C-H bonds, C-O bonds, C-C bonds, O-H bonds and C-N bonds -
All represent energy.
Carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen are called matter/ substances
The impala consumes this for gwroth for respiration. cheetah consumes the impala passing on the same molecules, reorganizes them into cheetah form and then to the lion who reorganizes them as well
Which are in the bonds between the elements.
cheetah is the secondary consumer
lion is the tertiary
Converts light energy to chemical energy.
Chemical energy takes the form of organic molecules including carbohydrates, proteins and lipids.
C-H bonds, C-O bonds, C-C bonds, O-H bonds and C-N bonds -
All represent energy.
Carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen are called matter/ substances
The impala consumes this for gwroth for respiration. cheetah consumes the impala passing on the same molecules, reorganizes them into cheetah form and then to the lion who reorganizes them as well
Which are in the bonds between the elements.
4.5b Food Webs
Allows us to provide a much better description of the ecosystem.
Food web allows us to show organisms feeding at different trophic levels.
Organisms can have different and multiple predators.
Organisms may be feeding on multiple pray.
Results in food all the chains will becoming linked.
Food web allows us to show organisms feeding at different trophic levels.
Organisms can have different and multiple predators.
Organisms may be feeding on multiple pray.
Results in food all the chains will becoming linked.
4.5a Food Chains
Food chain links : producer, primary consumers, secondary consumers and tertiary consumers.
Has only 1 organism shown of the tropic level.
In a food chain you cannot show an organism being an omnivore, cannot show more than 2 trophic levels.
Food chain shows the flow of matter and the flow of energy.
Has only 1 organism shown of the tropic level.
In a food chain you cannot show an organism being an omnivore, cannot show more than 2 trophic levels.
Food chain shows the flow of matter and the flow of energy.
4.4 Trophic Levels
Trophic: Means to feed.
Carrot plant: Photosynthesis
Carrot fly: Herbivore
Flycatcher: Carnivore
Sparrow Hawk: Top carnivore
Producer turns the light energy into chemical energy.
Primary consumer takes in the chemical energy of the plant into a chemical energy of the fly.
Secondary consumer chugs energy from 1 form to another.
Tertiary consumers eats secondary consumers which take in molecule.
All of these will die/decompose and will turn into bacteria and fungi.
Carrot plant: Photosynthesis
Carrot fly: Herbivore
Flycatcher: Carnivore
Sparrow Hawk: Top carnivore
Producer turns the light energy into chemical energy.
Primary consumer takes in the chemical energy of the plant into a chemical energy of the fly.
Secondary consumer chugs energy from 1 form to another.
Tertiary consumers eats secondary consumers which take in molecule.
All of these will die/decompose and will turn into bacteria and fungi.
4.3 Quadrates samples
Sample has to be random (no bias)
has to be representative (large)
A sample needs to be big enough so the estimate has to be close to the real population.
You will need a random numbers to generate on line or table. for x coordinate and y coordinate that will tell us where to take out sample from.
We need a representative sample. Bigger the better.
4.2 Quadrates
Sand Dune ecosystem is made up of number of population which forms community, habitat
quadrating can be made by any material
Quadrate is a method of sampling different location so that population can be compare between two location.
quadrating can be made by any material
Quadrate is a method of sampling different location so that population can be compare between two location.
4.1 Ecosystems
A community of organisms consist of a population of different species.
Habitat includes all the "Abiotic" factors (non biological factors) for example daylight, temp, rainfall, humidity, slope.
Population is the number of individuals of a particular species.
They are all non- biological.
Habitat includes all the "Abiotic" factors (non biological factors) for example daylight, temp, rainfall, humidity, slope.
Population is the number of individuals of a particular species.
They are all non- biological.
Sunday, April 24, 2011
3.4 Plant Fertilisation: Understand that the growth of the pollen tube followed by fertilization leads to seed and fruit formations.
- Pollen grains (on stigma) they germinate.
- The pollen tubes the nuclease travels down into the ovule. In other words pollen nuclease will fertilized the ovule which will form zygote which will grow into the abronia plant.
- Outside of the ovule forms the seed coat which is call TESTA.
- Inside of the ovule we also cotyledons which stored food for the seedings.
- The thickening of the wall which protects the ovary where the plants will put a lot of energy such as sugar, protein and built this up and this will form the fruit which is develop from the wall of the ovary or the carpal.
Sunday, April 3, 2011
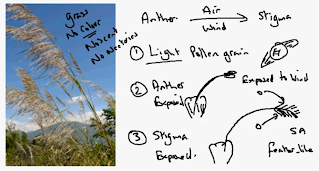
3.3b: Describe the structures of an insect-pollinated and wind- pollinated flower and explain how each is adapted for pollination.
- Transfers of the pollen grain from the anther to the stigma (through air and wind)
- These process will not occur if it does not consist of the following:
- Light pollen
- Anthers will hang well clear (Expose to the wind)
- Relates to the stigma (catch the pollen grain in the air trough the wind)
3.3a: Describe the structures of an insect-pollinated and wind-pollinated flower and explain how each is adapted for pollination.
- Pollination of a flower has to be transfer of pollen grains from the anther to the stigma of the other.
- Pollen is a male plant. These processes are transfer by insect. By the flowers attract the insect.
- If pollen goes trough one plant to another this is call cross-pollination.
- Flowers can attract insects by:
- Signal (colour petal)
- Scent (detected molecule)
- Value (produce sugar called fructose)
- Pollen it self as a source of protein.
Saturday, March 26, 2011
2.81 Phototropism: Describing Positive phototropism of stems
Photo referring to light.
Tropism referred to growth in response to light. Positive suggest that the growth is towards the light.
Light comes in from all direction therefore it will grow forwards.
If the light comes from the side (lateral) then the plants will bends in the growth towards the lights. (This is an example of positive tropism growth of the stems towards the lights) the light will then moves to the opposite side. This is know as auxin which causes more growth.
2.80 Geotropism: describing the geotropic responses of roots and stems
Geotropic referred to gravity and growth responses.
An embryonic root grows downward. This process is called Positive geotropism.
An embryonic roots grows upward is called Negative Geotropism
Shoots grow upwards and the roots grow downwards.
An embryonic root grows downward. This process is called Positive geotropism.
An embryonic roots grows upward is called Negative Geotropism
Shoots grow upwards and the roots grow downwards.
Friday, March 25, 2011
2.55 Rate of transpiration - Explain how the rate of transportation is effected by changes in humidity, wind speed and temperature and light intensity
Transpirtion is a loss of water through the leaf. This is cause by evaporation.
For this process to occur its need to be change from a liquid to a gas. Diffusion will then go through the stomatal pore.
The sunshine generates the heat. The heat will then transform the water of the leaf then into the gas.
Concentration of the gradient in the water is a big difference then then it will be high rate of transpiration.
If the humidity is low then the transpiration slows down. If the humidity is high you will get more evaporation.
For this process to occur its need to be change from a liquid to a gas. Diffusion will then go through the stomatal pore.
The sunshine generates the heat. The heat will then transform the water of the leaf then into the gas.
Concentration of the gradient in the water is a big difference then then it will be high rate of transpiration.
If the humidity is low then the transpiration slows down. If the humidity is high you will get more evaporation.
Thursday, March 24, 2011
2.79 Plants and stimuli
stimuli: changes in the environment e.g temperature or light changes.
Receptor: Is in a plant. Its function is to detect the stimuli. After this process will turn into response.
Response: often takes the form of growth. The response between stimuli and the growth is called the tropism.
Tropism: Involves light. This process is called phototropism.
This involves response to gravity. This process is called geotropism.
Receptor: Is in a plant. Its function is to detect the stimuli. After this process will turn into response.
Response: often takes the form of growth. The response between stimuli and the growth is called the tropism.
Tropism: Involves light. This process is called phototropism.
This involves response to gravity. This process is called geotropism.
Sunday, March 20, 2011
2 54 Transpiration
Recall the transpiration in the evaporation of water from a surface of a plant.
Evaporation will occur when go from liquid to gas. We will need Heat for this process. In addition to this heat is provided by sunlight.
Sunlight absorbed the leaf structure. So the light energy will be converted into hear.
The evaporation is through the stomatol pore.
Sunlight will have to go through the process of photosynthesis. + Not all lights will be absorbed in the chloroplast.
Above the stomatol pore there is phases change from liquid to gas à gas diffuses through the pore by a fairly steep diffusion gradient.
Sunday, March 13, 2011
2.53 How water is obsorbed by root hair cells
water uptake in the roots
- · Branches increase the surface area. It also absorbs water.
- · There are root hairs at the end of each root. You have to use microspores to see them. These roots are epidermis cell.
- · Root hair creates the surface area for absorption
- · Involves active transport of mineral + encourage plants to take up water by osmosis/ water moves from dilute to concentrated solution
- · Dilute is a soil of water surrounded the roots + concentrated creates to built up mineral in the cells
- · Water then moves in the plants to the xylem by osmosis.
Here is an example of a root structure:
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)