- Pollen grains (on stigma) they germinate.
- The pollen tubes the nuclease travels down into the ovule. In other words pollen nuclease will fertilized the ovule which will form zygote which will grow into the abronia plant.
- Outside of the ovule forms the seed coat which is call TESTA.
- Inside of the ovule we also cotyledons which stored food for the seedings.
- The thickening of the wall which protects the ovary where the plants will put a lot of energy such as sugar, protein and built this up and this will form the fruit which is develop from the wall of the ovary or the carpal.
Total Pageviews
Sunday, April 24, 2011
3.4 Plant Fertilisation: Understand that the growth of the pollen tube followed by fertilization leads to seed and fruit formations.
Sunday, April 3, 2011
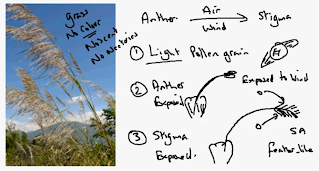
3.3b: Describe the structures of an insect-pollinated and wind- pollinated flower and explain how each is adapted for pollination.
- Transfers of the pollen grain from the anther to the stigma (through air and wind)
- These process will not occur if it does not consist of the following:
- Light pollen
- Anthers will hang well clear (Expose to the wind)
- Relates to the stigma (catch the pollen grain in the air trough the wind)
3.3a: Describe the structures of an insect-pollinated and wind-pollinated flower and explain how each is adapted for pollination.
- Pollination of a flower has to be transfer of pollen grains from the anther to the stigma of the other.
- Pollen is a male plant. These processes are transfer by insect. By the flowers attract the insect.
- If pollen goes trough one plant to another this is call cross-pollination.
- Flowers can attract insects by:
- Signal (colour petal)
- Scent (detected molecule)
- Value (produce sugar called fructose)
- Pollen it self as a source of protein.
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)